GUI Library (simion.experimental.dialog)¶
This library is for displaying dialog boxes and constructing basic GUI’s. The library is intended to be simple and quick to use. This library requires SIMION 8.2.
The library consist of a single function
simion.experimental.dialog.
This displays a simple dialog with no controls:
simion.experimental.dialog {}
This displays a dialog with some text:
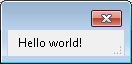
simion.experimental.dialog {'Hello world!'}
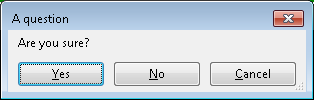
You can also include a title and buttons and record which button was clicked:
t = simion.experimental.dialog {
'Are you sure?',
title='A question',
buttons='&Yes|&No|&Cancel'
}
print(t.result) --> 'Yes', 'No', or 'Cancel'
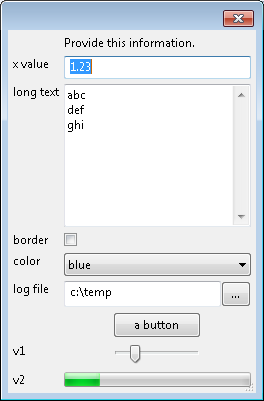
The dialog can input data from text boxes, check boxes, combo boxes, file input boxes, and other controls:
t = simion.experimental.dialog {
'Provide this information.',
{'x value', 1.23},
{'long text', 'abc\ndef\nghi', multiline=true},
{'border', false},
{'color', 'blue', values={'red', 'green', 'blue'}, type='choice'},
{'log file', [[c:\temp]], type='file'},
{'a button', nil, type='button'},
{'v1', 0.2, type='slider'},
{'v2', 0.2, type='progress'},
title='sample controls'
}
print(t['x value'], t.border, t.color, t['log file'])
You can define an event handler function that will respond to changes and modify control values:
simion.experimental.dialog {
'Enter two numbers to sum:',
{'x', 1.23},
{'y', 2.34},
{'-', id='sum'},
{'clear', type='button'},
update = function(data, event)
if event.id == 'clear' then data.x = 0; data.y = 0 end
if type(data.x) == 'number' and type(data.y) == 'number' then
data.sum = data.x+data.y
end
end,
modal=false
}
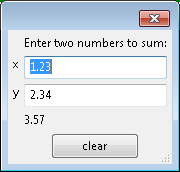
You can make a “mode-less” (not modal) dialog with modal=false.
This means it doesn’t wait until the dialog closes
but returns immediately and allows other windows to still be used.
local w
w = simion.experimental.dialog {
{nil, '', type='text', multiline=true, id='text'},
modal=false,
update=function(data,event)
if event.type == 'close' then print 'bye' end
end
}
for i=1,3 do
simion.sleep(1)
w:update(function(data,event)
data.text = data.text .. math.random() .. '\n'
end)
end
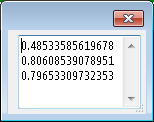
A modeless dialog immediately returns the window object w, which
has a method w:update that can be used to update the window.
Passing no arguments causes the update function (if any) to be
invoked; alternately, you can pass it a different update function,
as shown above.
dialog function¶
The dialog function has this interface.
- simion.experimental.dialog()¶
data = simion.experimental.dialog {
controls...,
modal=modal,
buttons=buttons,
update=update,
}
controls...is a comma separated list of controls to display in the dialog. The controls are displayed in the order given. See “Control Types” below.modalis whether to display as a modal (true) or mode-less (false) dialog. The default istrue. A modal dialog does blocks (does not return) until the user closes the dialog. A mode-less dialog returns immediately and allows other windows still to be used.updateis an event handler function of the formfunction(data,e)wheredatais a table of control ID’s and their corresponding values.dataalso contains the valuedata.titlecontaining the dialog box’s title. Changes todatawithin theupdatefunction will result in the display being updated accordingly (currently, you can only change control values in the update function but cannot add or remove controls themselves).eis the event object with valuese.typeande.id.e.typeis the type of the event:'create'- called when dialog is first created.'close'- called when dialog is being closed or requested to close.event.idwill contain the ID of the button used to close the dialog (orCancelif closing without a button such as by pressing the ESC key or X in the title bar). Ifupdatereturnsfalsewhen a button that is not a cancel button is pressed, then the dialog will not be closed.'change'- a value in a control has changed.event.idwill contain the ID of the control that has changed.'update'- caused by a call to window:update.
e.idis the name of the control that caused the event ornilfor event types like'update'that are not associated with any specific to a control.Example:
update=function(data,e) data.title = e.type..' '..tostring(e.id) end.buttonsis a string containing a list of button labels separated by the|character. These display at the bottom of the dialog. The first button is understood as an OK button. The last button (if more than one button) is understood as a Cancel button (and responds to the ESC key). Example:'&Yes|&NO|&Cancel'.
Control Types¶
Most controls have the form
{label, value, type=type, id=id, help=help}
typeis a string indicating the type of control to create. The control types are described later below. If omitted (nil) it infers the control type based onvalue:If
valueis a string or number, thentypewill betext.If
valueis a boolean, thentypewill becheckbox.If
valueis omitted (nil), thentypewill bestaticandlabelwill be used as the value.
labelis a string that will be displayed before the control. It will also serve as the identifieridifidis not specified.idis a string that identifies the control in the code. If omittednil, it defaults to thelabelgiven (but stripping out any ‘&’ characters).idwill be the key in thedatatable (returned bysimion.experimental.dialogor passed to anupdatefunction) to access the corresponding value (data[id]).valueis the initial value for the control. It defaults tonil. The data type ofvalueis also recorded, and if it is a number or boolean, then any new value written to thedatatable will be represented in the same type if it is possible to do so; otherwise, thedatatable will contain a string value.helpis a string of help text (almost like a tooltip) displayed when the focus is on the control. It defaults tonilfor no help.

Static Text¶
{label, value, type='static', id=id, help=help}
{label, type='static', id=id, help=help}
{text} -- short-hand form
text -- short-hand form
This creates a static text control. It is used for displaying a string that the user cannot change.
label is a string to display.
Examples:
{'the text:', 'some text', type='static'} -- static text with label
{'some text', type='static'}
{'some text'} -- short-hand, equivalent to above
'some text' -- short-hand, equivalent to above
Text Control¶
{label, value, multiline=multline, type='text', id=id, help=help}
This creates a text box control. It is used for entering a string (single or multi-line) or number.
valueis string, number, boolean, ornil.multilinedetermines (true/false) whether this is a multline text box or not (defaultfalse). A multiline text box allows new linse to be included and usually contains multiline lines.
Examples:
{'my value', 'some text', type='checkbox'}
{'my value', 'some text'} -- short-hand
{'my value', 1.23}
{'my value', true, type='text'}
{'my value', '123\n234\n345', multiline=true}
Check Box¶
{label, value, type='checkbox', id=id, help=help}
This creates a check box.
It is used for entering a boolean value (true/false).
valueis a boolean (true/false). It defaults tofalse.
Example:
{'my value', true, type='checkbox'}
{'my value', true} -- short-hand
File Input Control¶
{label, value, type='file', wildcard=wildcard, id=id, help=help}
This creates a file input control.
It consists of a text box (like type='text') for entering
a file name and a button that can be clicked to select a file
from a dialog box.
The text box also supports autocompletion of file names.
An optional wildcard field allows limiting the
selected files to certain types and consists
of pairs of textual descriptions followed by the wildcard, separated
by | characters
(e.g. "Text File (*.txt;*.csv)|*.txt;*.csv|Other (*.*)|*.*");
Example:
{'my file', [[c:\\temp]], type='file'}
{'my file', [[c:\\temp]], type='file',
wildcard="Text File (*.txt;*.csv)|*.txt;*.csv|Other (*.*)|*.*"}
Choice Control¶
{label, value, values=values, type='choice', id=id, help=help}
This creates a choice box, for selecting a value from a drop down list.
values is a list of values in the choice box, and value
should be one of the values (defaults to the first value if omitted).
value will be nil if no item is selected.
Example:
{'color', 'blue', values={'red', 'green', 'blue'}, type='choice'}
The values array can be edited at runtime using the
key id..'_values' in the data table:
simion.experimental.dialog {
{'x', 0, values={0}, id='x', type='choice'},
update = function(data, e)
table.insert(data.x_values, math.random())
end
}
Slider¶
{label, value, type='slider', id=id, help=help}
This creates a slider control, which is like a scroll bar to select
a value.
The value ranges between 0.0 and 1.0, will be truncated if
outside this range, and defaults to 0.0 if nil.
Example:
{'my value', 0.2, type='slider'}
Progress Bar¶
{label, value, type='progress', id=id, help=help}
This creates a progress bar.
It can be useful for displaying the percent complete
for some operation.
The value ranges between 0.0 and 1.0, will be truncated if
outside this range, and defaults to 0.0 if nil.
Example:
local w = simion.experimental.dialog {
{nil, 0.0, type='progress', id='p'},
modal=false
}
for i=1,10 do
simion.sleep(0.3)
w:update(function(t,e) t.p = t.p + 0.1 end)
end
Other Notes¶
An
updatefunction may callsimion.sleep(), and if a request is made to close the window during the sleep, that request is ignored. This prevents the window being destroyed when an event handler is currently being processed.
TODO¶
Limitations/Possible extensions:
Currently there is no way to add/remove controls after the dialog is created. Perhaps this is not commonly needed.
The layout is currently limited to placing the controls in a vertical list with labels, like a property sheet.
Possibly add other control types.
See Also¶
SIMION Example: gui - examples of using this library.
Changes¶
8.2EA-2017-01-30: Reuse same table for
simion.experimental.dialogreturn value andupdatefunction. Useful formodal=trueso that return table updates as GUI is changed.8.2EA-2013-04-30: Allow changing choice control values during
update. Add wildcard to file control. Allow label on static text.8.2EA-2014-04-14, initial version