Time of Flight¶
A time of flight mass spectrometer first accelerates particles to a given kinetic energy (KE) with an electric field. At the end of the acceleration region, particles will have obtained the same KE but different velocities depending on mass (KE = (1/2) m v^2). The particles are then flown through a field free region. Due to their different velocities, they arrive at the detector at different times, which allows measuring their mass to charge (m/z) ratio.
SIMION Specific¶
See the SIMION Example: tof - basic TOF example in SIMION.
Screenshots are below.
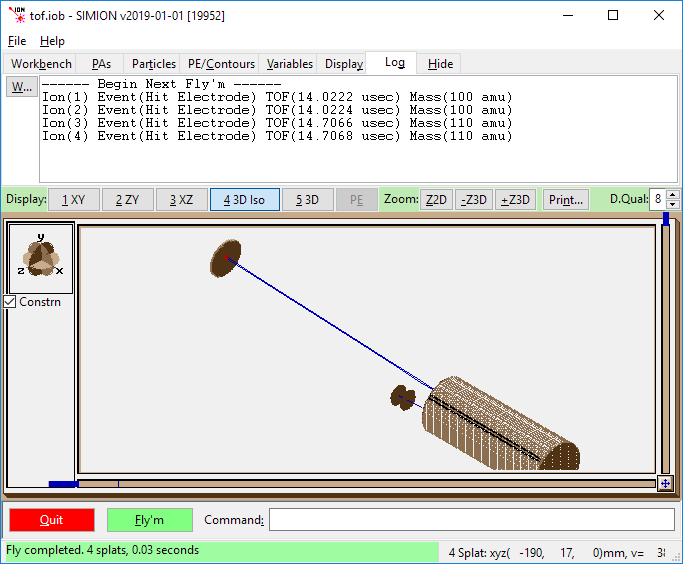
3D view of time of flight system.
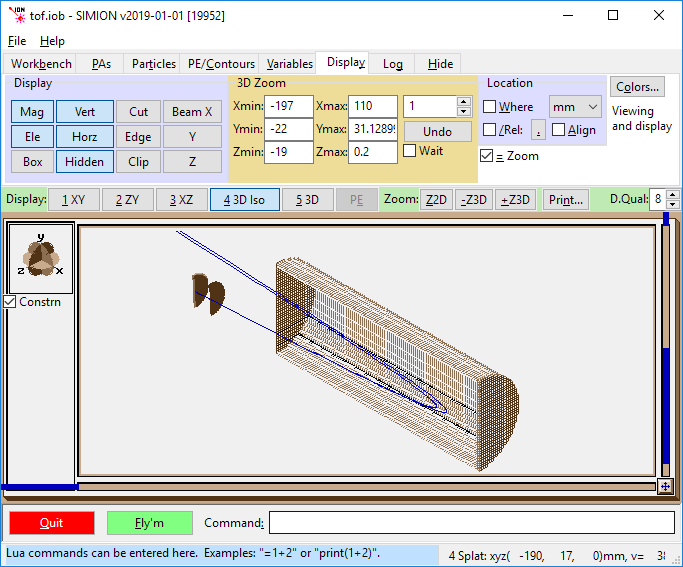
Cutway to see particle inside reflectron.
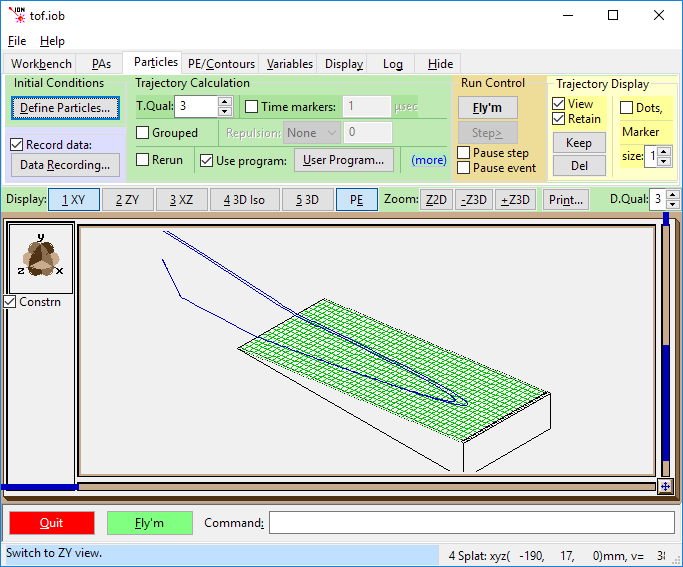
PE view of reflectron.
Reflectron¶
A reflectron reduces variability in flight time of particles with the same mass but variable energy. Particles with larger energy travel further into the reflectron.
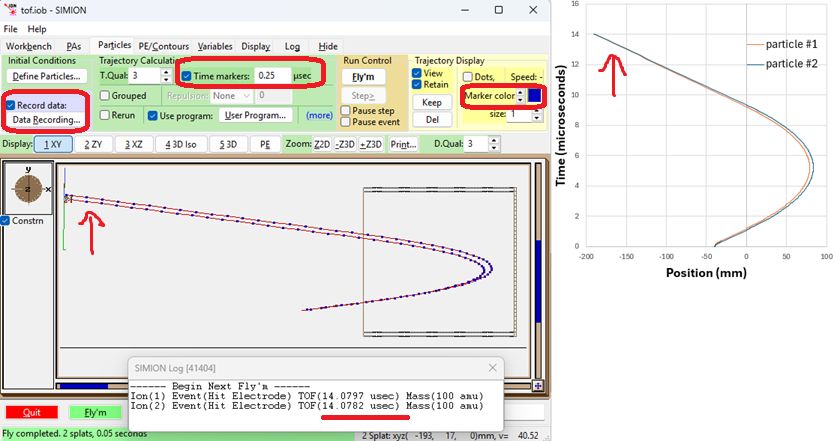
Time markers may be used to visualize the spread in flight time [1], or you can use Data Recording to plot time v.s. position at every time step. Below shows this using SIMION Example: tof:
See Also¶
Session 4 “Time of Flight” in the Short ASMS Course (
courses\shortfolder in the SIMION 8.0 program directory and also included in SIMION 7.0).Wiley, W. C., & McLaren, I. H. (1955). Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer with Improved Resolution. Review of Scientific Instruments, 26(12), 1150–1157. doi:10.1063/1.1715212 | pdf