Field Emission¶
Field emission (FE) is a process in which a metal surface will emit current when that surface is exposed to a sufficiently high electric field (typically on the order of 1 V/nm and under high vacuum to avoid an Electric Arc). The emission current density is a function of the cathode material work function and the local electric field magnitude over the surface and can be approximated by the Fowler-Nordheim equations, of which there are multiple variants. One way to generate the high fields required without resorting to high voltages is to start with a much weaker field generated by cathode and anode plates and between these place a tiny sharp electrode, typically in the form of a cone or tube with radius of curvature at the tip on the order of 1 micrometer. Fields near the tip can, because of the field curvature, be orders of magnitude larger than the surroundings, and this amplification factor is called the field enhancement factor. A pure field emission is called cold field emission (CFE), but at higher temperatures, a combination of thermionic and field emission called Schottky emission ([1]) can occur.
Simulation¶
See SIMION Example: field_emission [added in 8.1.1.0] for details on simulation. This illustrates some ways to handle problems of this nature and special techniques with the geometry and emission.
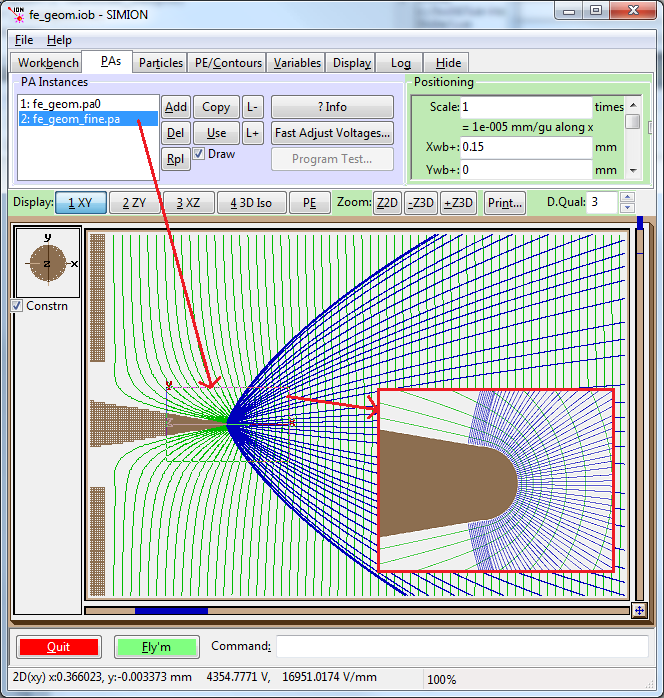
Fig. 83 Figure: illustration of SIMION Example: field_emission, of optionally obtaining better accuracy with fine PA nested in coarse PA.¶
CPO¶
Field emission is one area where the CPO-3DS software (http://simion.com/cpo) excels. CPO uses the BEM method, which handles the large differences in geometric scale in an accurate and relatively straightforward way (simpler than FEM because it is only requires a surface mesh, not a volume mesh), for 2D and 3D, including high field accuracy field calculations on the surfaces and applying the Fowler-Nordheim emission on those surfaces.
See Also¶
SIMION Example: field_emission [added in 8.1.1.0]
Southard, A.E.; Getty, S.A.; Costen, N.P.; Hidrobo, G.B.; Glavin, D.P. “Understanding the effect of electron gun geometry on emission characteristics for the purpose of optimizing the VAPoR time-of-flight mass spectrometer,” Microsystems for Measurement and Instrumentation (MAMNA), 2012 , vol., no., pp.1-4, 27-27 March 2012 doi:10.1109/MAMNA.2012.6195104 – paper using SIMION 8.1 for field emission cathode.
LiCheng2016. Li, Detian; Cheng, Yongjun; Zhang, Huzhong; Wang, Yongjun; Sun, Jian; Dong, Meng. Investigation of an extractor gauge modified by carbon nanotubes emitter grown on stainless steel substrate. Vacuum. volume 123, year 2016, pages 69-75. doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2015.10.016 - carbon nanotube ion guage studied in SIMION 8.0. 100 million points.