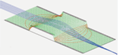
Lens¶
SIMION has often been used to simulate 2D and 3D lens systems, either in isolation or as components of other systems. The three-element Einzel lens example in SIMION is demonstrated in A Tour of the SIMION Demo.
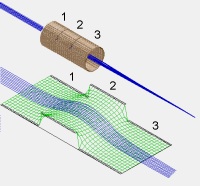
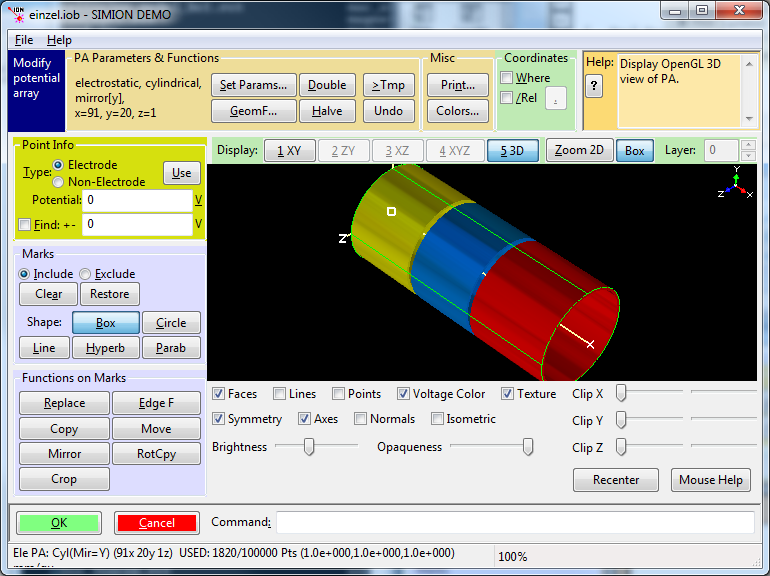
Fig. 38 Figure: SIMION Einzel lens example (above) with corresponding potential energy surface (below).¶
Some papers covering the simulations of lenses in SIMION include
Multi-element electrostatic lens systems for focusing and controlling charged particles Omer Sise, Melike Ulu, and Mevlut Dogan. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A. Volume 554, Issues 1-3, 1 December 2005, Pages 114-131. (Department of Physics, Science and Arts Faculty, Afyon Kocatepe University, Turkey.) dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2005.08.068; [arxiv](http://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0503145 online preprint) (Additional material on Omer Sise’s home page).
Evaluation of aberrations of immersion objective lenses in relation to electron emission microscopy Bernheim M. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 193-204 (2006)
Image acquisition with immersion objective lenses using electrons emitted with several tenths of an electron volt energies: Towards high spatial resolution ESCA analysis Bernheim M. Ultramicroscopy 106 (2006) 398-412
Aberration coefficients of multi-element cylindrical electrostatic lens systems for charged particle beam applications Omer Sise, Melike Ulu and Mevlut Dogan. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 573/3 (2007) 329-339
Characterization and modeling of multi-element electrostatic lens systems Omer Sise, Melike Ulua and Mevlut Dogan. Rad. Phys. Chem. 76/3 (2007), 593-598
Exploring focal and aberration properties of electrostatic lenses through computer simulation Omer Sise, David Manura and Mevlut Dogan. Omer Sise et al 2008 Eur. J. Phys. 29 1165-1176 – introduction to lens property simulations in SIMION, from a teaching perspective.
Computer simulation of electrostatic aperture lens systems for electron spectroscopy Omer Sise, Nimet Okumus, Melike Ulu and Mevlut Dogan. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena. 15 August 2009
Electron Focusing Lens for a Modulated X-Ray Source (2011 Olin-NASA Research Group). This provides a detailed, day-by-day account of the trial-and-error process of designing, simulating in SIMION, constructing, and testing an Einzel lens. GEM files are included on the Documentation page (Prototype simulation files).
LiuNicolas2013. Design of a lens table for a double toroidal electron spectrometer Liu, Xiao-Jing; Nicolas, Christophe; Miron, Catalin. Design of a lens table for a double toroidal electron spectrometer. Review of Scientific Instruments, volume 84, issue 3, year 2013, pages 033105. – calculates lens tables by iterating over voltages in SIMION 8.0
The voltage optimization of a four-element lens used on a hemispherical spectrograph with virtual entry for highest energy resolution O. Sise, G. Martínez, I. Madesis, A. Laoutaris, A. Dimitriou, M. Fernández-Martín, T.J.M. Zouros. – four-element lens optimization together with hemispherical deflector analyzer (HDA) and PSD detector, with SIMION FDM as well as BEM following by experimental confirmation.
Theory¶
Helmholtz-Lagrange Law¶
The Helmholtz-Lagrange Law relates the linear magnification
M and angular magnification m of rays through an electrostatic
lens to the ratio of potentials between the two ends of the lens.
Linear magnification is 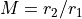 , where
, where
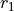 and
and 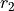 are the
displacements from the axis of the object and image locations.
Angular magnification
are the
displacements from the axis of the object and image locations.
Angular magnification 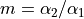 ,
where
,
where 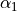 and
and 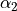 are the pencil
angles of the object and image points.
The pencil angle is the half angle of the beam.
are the pencil
angles of the object and image points.
The pencil angle is the half angle of the beam.
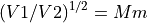
See the SIMION Example: lens_properties for an example of Helmholtz-Lagrange Law.
Snell’s Law¶
See Light Optics and SIMION Example: lens_properties for a demonstration of Snell’s law.
Cardinal Points¶
Carinal points describe a lens. The symbols as commonly used by Heddle and elsewhere are given below.
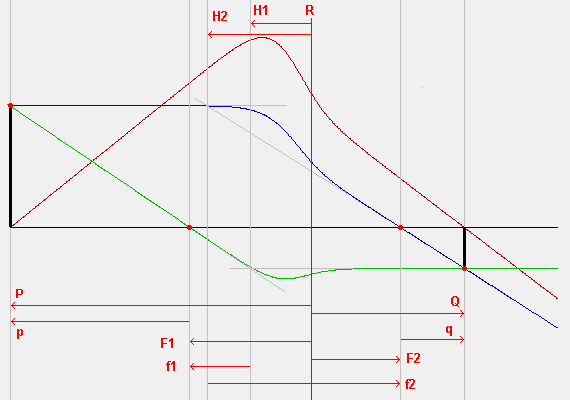
Fig. 39 Figure: Cardinal points in a lens, demonstrated with SIMION particle traces in SIMION Example: lens_properties¶
R - reference plane. The location of this plane is arbitrary, but it is usually, by convention, taken as the center of the center lens and defined as x=0.
P - object position. This is the location of the object being imaged. It is relative to R. The principle rays intersect here.
Q - image position. This is the location of the image of the object P. It is relative to R. The principle rays intersect here too.
F1 - first focal point (mid-focal distance). This is the location of the intersection of second principle ray and axis. It is relative to R.
F2 - second focal point (mid-focal distance). This is the location of the intersection of the first principle and axis. It is relative to R.
H1 - first principle plane. This is the location of the intersection of the second principle ray asymptotes. One of the asympotes may be approximated as the tangent of the ray through F1 (assuming the lens is not too strong).
H2 - second principle plane. This is the location of the intersection of the first principle ray asymptotes. One of the asympotes may be approximated as the tangent of the ray through F2 (assuming the lens is not too strong).
p - This is the distance of P relative to F1.
q - This is the distance of Q relative to F2.
See SIMION Example: lens_properties for more information and an example.
Screenshots¶
Einzel lens geometry (three cylindrical lenses), from SIMION Example: einzel.
Equipotential lines showing electric field.
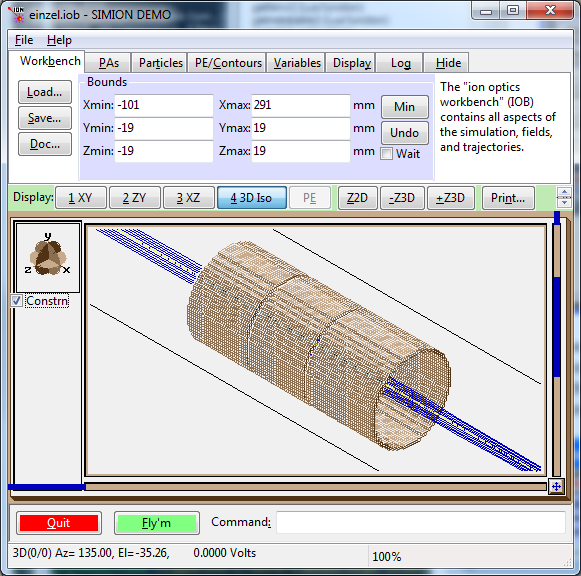
Particles flying through lens.
See also A Tour of the SIMION Demo.
See also¶
Pictures of a real einzel lenses: Einzel lens (Purdue PRIME Lab, Department of Physics); here (DREBIT HCI-irradiation facility); here (Miniature einzel lens - Imperial College London)
Electrostatic Lens Systems D W O Heddle.
Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences, volume 29A, chapter 5 Electron and Ion Optics by George C. King is a short 18 page summary of lens theory, similar to Heddle.
SIMION Example: lens_properties: various SIMION examples analyzing lens focusing
SIMION Example: tune: lens voltage optimization. SIMION Example: geometry_optimization looks at geometry optimization too.
MassSpecPro.com: Einzel lens - tutorial with SIMION pictures.