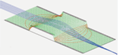
Magnetic Sector¶
A charged particle (mass m and charge q) with velocity v perpendicular to a uniform magnetic
field B will (by the Lorentz Force Law) experience a
centripetal force 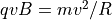 , sustaining a circular motion of
radius R in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field [4] [3] .
This equation is called the cyclotron formula [1] [2],
and it may be rewritten as
, sustaining a circular motion of
radius R in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field [4] [3] .
This equation is called the cyclotron formula [1] [2],
and it may be rewritten as 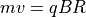 , thereby showing that the
gyroradius [2], R, is proportional to momentum, if charge is constant.
A uniform magnetic field
therefore can act as a momentum analyzer (in contrast to electric fields used in
kinetic energy analyzers like in the Hemispherical Deflection Analyzer (HDA)).
, thereby showing that the
gyroradius [2], R, is proportional to momentum, if charge is constant.
A uniform magnetic field
therefore can act as a momentum analyzer (in contrast to electric fields used in
kinetic energy analyzers like in the Hemispherical Deflection Analyzer (HDA)).
A magnetic sector is a type of mass analyzer using
a static magnetic field to deflect particles in this way along a roughly circular
arc. It is characterized by a deflection angle 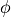 and radius
and radius 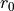 .
For background/theory, particularly on focusing properties in design, see [5]
[6] [7].
.
For background/theory, particularly on focusing properties in design, see [5]
[6] [7].
See also Hemispherical Deflection Analyzer (HDA), which is combined with a magnetic sector in a double focusing magnetic sector.
SIMION specific¶
See SIMION Example: magnet (mag90.iob) for a simple 3D simulation with cylindrical poles
and fringing fields. SIMION Example: magnetic_sector (added in 8.1.1.0) is a more
extensive example, which examines focusing properties of various magnetic sector
geometries (inclined and conical, 2D and 3D)
with full control of parameters. The HIPIRMS course [8] includes
other SIMION magnetic sector models and discussions.
The Short ASMS Course (courses\short) (Session 2) has a brief look at
sectors.
SIMION simulations of sectors are
illustrated in the discussions in [6]. Magnetic poles with approximately infinite
permeability and treated with scalar magnetic potential are the easiest to handle
(see Magnetic Potential).
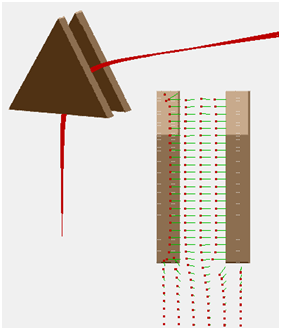
Fig. 46 Figure: SIMION Example: magnetic_sector - 60 degree 3D sector (with fringe fields) and B-field vectors.¶
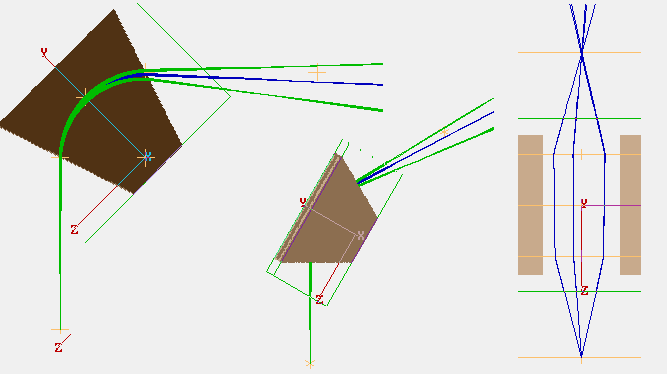
Fig. 47 Figure: SIMION Example: magnetic_sector - 90 degree 3D sector (with fringe fields) and inclined 26.56 degree entrance/exit angles to achieve symmetric stigmatic focusing.¶